
by Sameer Padhan, Practice Manager - Integration
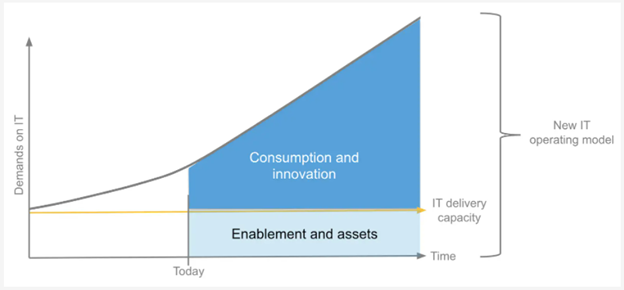
Company leaders and executives visualize and target to move rapidly and swiftly. To incorporate the demand from businesses, IT Engineering teams must move at the same pace. With a constant investment into IT, delivery for demands keeps on going up. Look at the last few years, IT has to manage cloud, SaaS applications and platforms, IoT, big data, etc. Also, competition is cutthroat. If businesses don’t improve their technology solutions, they will bite the dust. The difference between Business demands and IT delivery capacity is Delivery Gap.

With point-to-point applications connections, it becomes complicated with time and makes centralized IT slow.
The solution is both a modern platform and a new approach that decouples core IT projects from the innovation that happens within each line of business. This approach enables central IT to focus on operating, connecting, and abstracting systems of record. Subsequently, line of business IT benefits by consuming previously built assets and then extending those resources into new solutions, ultimately delivering customer-facing innovation. This enables a model for production, consumption, and feedback—a proven method of closing the IT delivery gap. This is achieved by Application Networks.
An application network is not just about building applications and sticking them together with APIs. What it really represents is a cultural shift. Many businesses want to understand how to organize themselves to be agile. The key to achieving agility is not how many assets are present on the application network but, rather, how many consumers are getting value from it.
By now, you might be a little confused about who has to do what then?
Let us show you three broad categories:

Who is going to oversee that everything is running smoothly? Enter C4E.
C4E is the Center for Enablement team which acts as a bridge between the Central IT, LOB IT, and App Developers. This team enables other teams to reduce the delivery gap. This team focuses on Governance, Asset Reusability, and Emphasizing Consumption.
C4E Team ensures:
With the usage of application networking and implementation of the proposed operating model, the Delivery Gap can be reduced.
At GyanSys our focus is to sustain long-term business success with innovative cross-cloud solutions. We transform our clients’ challenges into user-friendly solutions and accelerate digital transformation. Experts in our field, we bring a wealth of technology and business process knowledge to maximize your investments through our blended global delivery model to give your teams the tools to hit the ground running from day one. Contact us today to find out how we can work together.